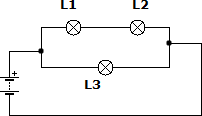
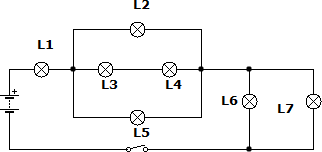
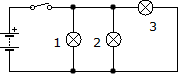
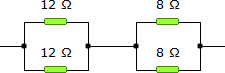
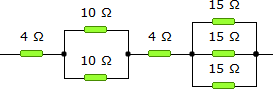
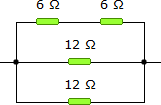
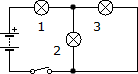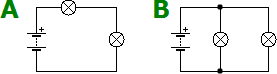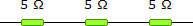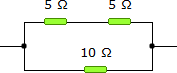19.
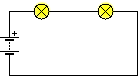
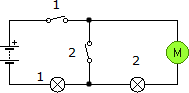
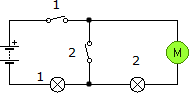
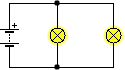
Suppose we have two circuits made up of identical elements: a battery, two lamps and a switch. In the first the connection of the receivers is done in series, while in the second it is done in parallel. In which circuit will the battery run out first?