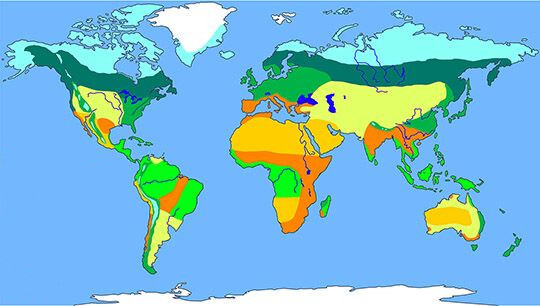
Grassland
Grasslands are biomes determined by the scarcity of rainfall and periods of droughts. Lands are dominated by grasses. Grasslands provide food for large herbivorous mammals.
Desert
Precipitation is scarce, so vegetation is almost nonexistent. Species have adapted to preserve the water they absorb during episodes of very poor rainfall. They have all had to adapt their activity to extremely dry conditions.
Tropical rain forest
Tropical rain forests are the most widely diverse biome. Abundant rainfalls allow the development of dense forests with very tall trees.
Polar ice
Polar ice regions have a permanent layer of ice all year round. There is no vegetation and only a few animals live there-
Savanna
Savannas are grasslands scattered with shrubs and isolated trees. Big mammals that feed on this vegetation, which in turn are the food supply for the populations of large predators.
Taiga
Taiga is a forest of coniferous trees which have adapted to live through long, very cold winters. Tiny rodents and birds feed on their seeds, and predators feed on these small animals.
Temperate forest
This forest typically includes deciduous trees. Climate in spring and summer favors the activity of insects, tiny birds, and mammals, which in turn are food for predators.
Mediterranean forest
These relatively small areas are covered by shrubs and some tree species that have leaves through out the year. Dry summers limit the activity of these ecosystems,
Artic Tundra
Vegetation in tundras includes lichens and moss, small herbaceous plants, and dwarf shrubs. Herbivorous animals are adapted to survive the cold winters there.