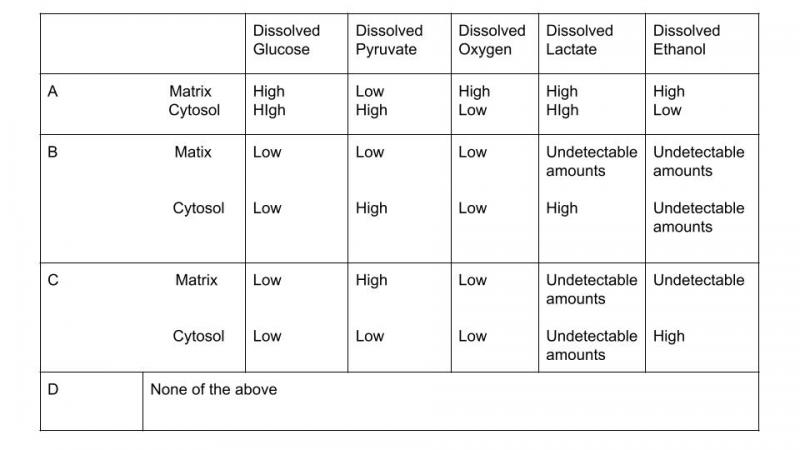
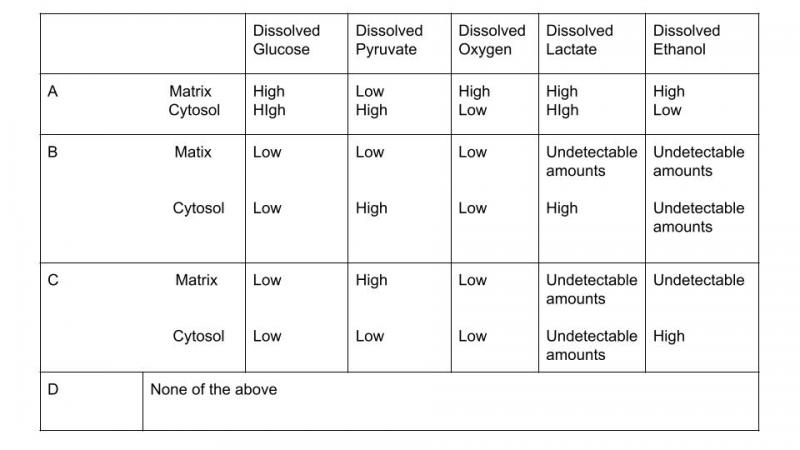
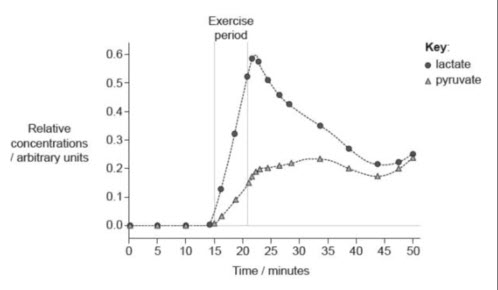
1.
A predominant genus of bacteria found in the human gut is microbiota. These anaerobic bacteria undergo fermentation in the gut, converting otherwise nondigestible carbohydrates into fermentation products that are used by the host for energy. Which of the following would most likely disrupt carbohydrate metabolism in these bacteria?